The SEO industry has a habit of panicking every time Google introduces a new feature. We’ve seen it with featured snippets, knowledge panels, and voice search.
Now, with the rise of AI-powered search experiences and large language models (LLMs), the panic has reached fever pitch once again. But perhaps for good reason this time – this is the biggest change to search we’ve ever seen.
Enter the latest acronym: GEO, or generative engine optimisation, also known as:
- AEO (Answer Engine Optimisation)
- AIO (Artificial Intelligence Optimisation)
- LLMO (Large Language Model Optimisation)
- Generative Search Optimisation (GSO)
- AI-SEO
The first thing to understand is that GEO and SEO share the same foundational principles. If you’re already following SEO best practices, you’ve built a solid foundation for AI search experiences too. There’s significant crossover between the two disciplines.
However, while the foundations align, there are unique factors we need to consider for GEO, and the way we measure GEO success can differ substantially.
Let’s explore these shared principles, where they diverge, and what this means for your strategy.
What are LLMs and why do they matter for search?
Large Language Models are AI systems trained on vast amounts of text data that can understand context, generate human-like responses, and combine information from multiple sources.
Some examples of the best-known LLMs are ChatGPT, Gemini, Perplexity and Copilot, and they often power SERP features for traditional search engines – Gemini powers Google’s AI Overviews, and Copilot powers Bing’s Generative Search.
These models don’t just match keywords anymore: they understand intent, context, and the relationships between different pieces of information. This is what makes them revolutionary for search, and why there are some unique methods to GEO that aren’t used in regular SEO strategies, and what makes reporting on GEO a whole new ballgame.
According to research from Semrush, LLMs are expected to have more traffic compared to traditional organic search by early 2028. Coupled with the anticipation that Google will, sooner or later, switch its default search mode to AI Mode, it’s hugely important that your organic search strategy is prepared for this.
Where is the crossover between SEO and GEO?
LLMs are trained on massive training datasets compiled from many sources, including web pages, books, and other text, but when they need to access real-time information or verify answers they often use the index of Google and/or Bing. This means they’re essentially reading the same search results that you’re already optimising for.
A great illustration of the crossover between SEO and GEO is the studies into the crossover between AI Overview citations and the top 10 organic search results. Recent studies have found that between 52% and 76% of AI Overview citations also ranked in the top 10 organic search results.
In some ways, LLMs can be thought of as a new postman delivering your content to users in a different format. If you’re ranking well and optimising for traditional search engines, it’s highly likely that your information and content will get picked up and referenced by LLMs.
Key strategies that underpin both SEO and GEO include:
- Clear, structured content that answers specific questions
- Comprehensive information that covers topics in depth
- Authoritative signals like expertise, trustworthiness, and proper citations
- Accessible website architecture that both humans and machines can navigate
- Semantic relationships between your content and related topics
As Google’s Danny Sullivan put it: “Good SEO is really having good content for people.” When you write clearly, cover topics comprehensively, and create something genuinely useful, you’re simultaneously optimising for traditional search engines, AI overviews, and LLM citations.
Key differences between SEO and GEO
1. Measurement and KPIs
Traditional SEO metrics are well-established: rankings, organic traffic, click-through rates, and conversions. We know what success looks like and how to measure it. GEO measurement, however, is still evolving and requires different tools and approaches.
Google Analytics remains the number one source of truth for LLM performance data. At GrowRoom, we’ve built a custom dashboard that pulls all LLM traffic data from GA4, allowing us to track when users arrive from AI platforms like ChatGPT, Perplexity, or Gemini.
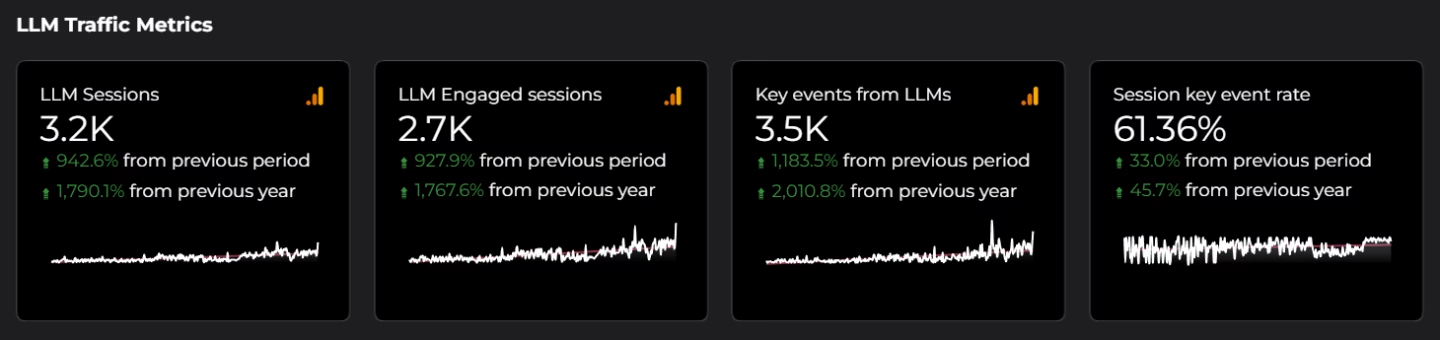
To then get a deeper understanding of GEO performance, we gauge our clients’ visibility across relevant pre-set prompts, tracking whether brands are being mentioned and how prominently. We also deploy custom GPTs and Gemini Gems to assess brand sentiment within LLM responses – understanding not just if you’re being mentioned, but how you’re being portrayed.
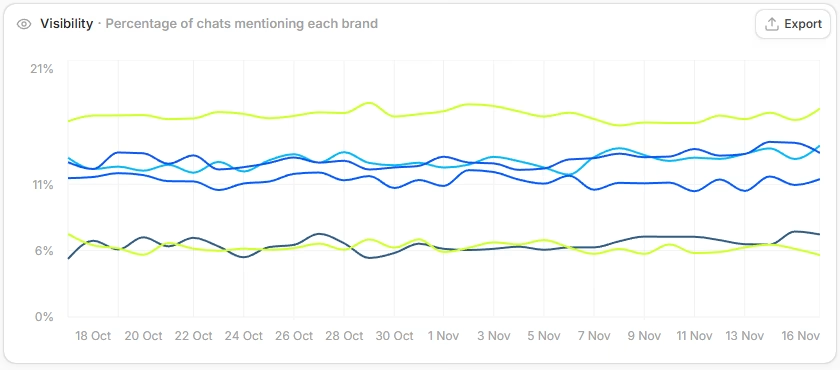
This multi-layered approach means:
- Tracking LLM referral traffic through GA4
- Monitoring citation frequency across relevant queries
- Assessing brand sentiment in AI-generated responses
- Measuring visibility against competitor mentions
Unlike SEO where rankings are relatively straightforward, GEO success requires monitoring how AI systems perceive, cite, and recommend your brand across countless conversational queries.
2. Influencing brand sentiment
For SEO, brand sentiment centres on demonstrating E-E-A-T (Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness) to search engines. This remains important for GEO, but LLMs form brand opinions through a different lens: the aggregate of what they’ve learned about you across the internet.
Brand sentiment in LLMs is heavily influenced by citations and how consistently your brand messaging appears across sources. If your brand repeatedly appears in “top” listicles with positive sentiment – whether on third-party sites or your own – LLMs learn to associate you with quality and leadership in your category. When Reddit users genuinely recommend your product or service in response to real questions, that carries enormous weight.
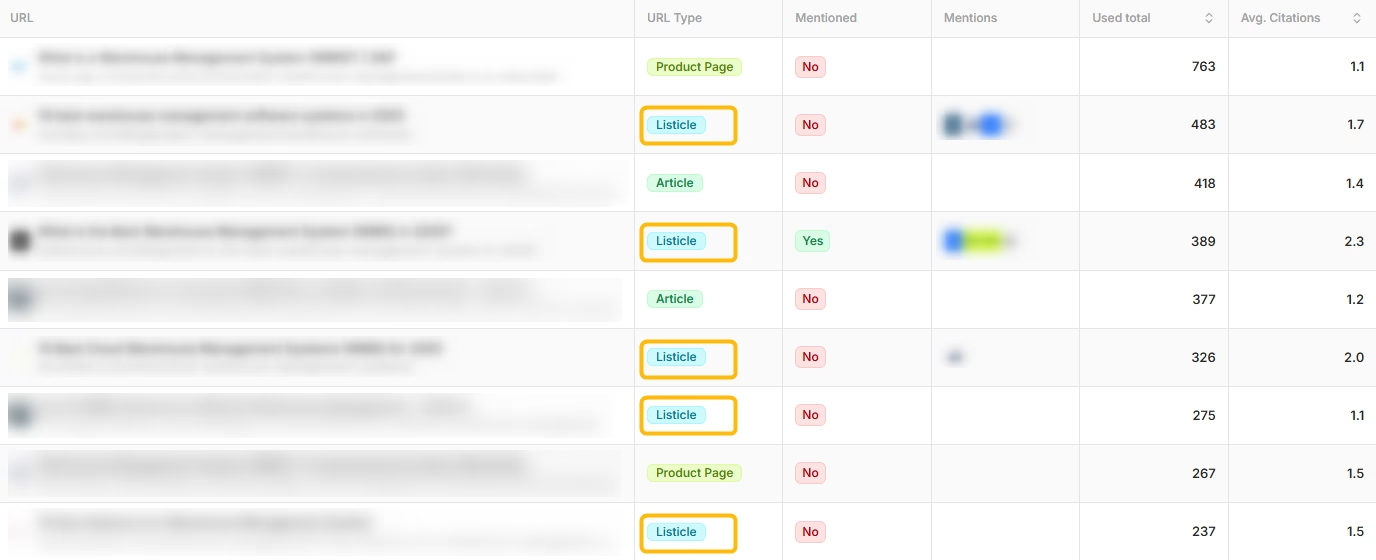
These platforms aren’t just backlink opportunities anymore; they’re teaching AI systems what to think about your brand. A single highly-engaged Reddit thread where users authentically praise your service can do more for your GEO than dozens of traditional press releases.
Building positive brand sentiment for GEO means:
- Ensuring your brand messaging is consistent across all platforms
- Earning placements in authoritative “best of” and comparison content
- Fostering genuine community discussions on platforms like Reddit
- Creating content that others naturally want to cite and reference
Where SEO focuses on signals to algorithms, GEO requires shaping the narrative that AI systems encounter about your brand across the entire internet.
3. Content format – AI crawlers don’t interact with Javascript
Semantic HTML has always been beneficial for SEO, and while Googlebot has learned to render and execute JavaScript effectively, LLM crawlers can’t (yet). AI systems typically access only the raw HTML delivered from your server, without executing any client-side JavaScript. If your critical content only appears after JavaScript runs, LLMs will never see it.
This means you need either server-side rendering (SSR), pre-rendering to deliver content in the initial HTML payload, or – the most reliable solution we suggest to all of our clients – semantic HTML from the start.
You can test your content with JavaScript disabled or check “view source” to see what LLMs actually see, and ensure your most important content is accessible in the initial HTML response.
4. Search engines index new content faster than LLMs
When you publish new content, Google can discover and index it within hours, sometimes minutes if your site has strong authority and crawl frequency. Submit your URL through Search Console, and you can often see it appearing in results within a day.
LLMs work on a fundamentally different timeline. The knowledge bases that power ChatGPT, Claude, Gemini, and other AI systems are updated periodically – not continuously. This means there’s an inherent lag between when content is published and when it becomes part of an LLM’s knowledge base. That lag can be weeks or even months.
This temporal gap has strategic implications. While your brand-new blog post about an industry development might rank in Google tomorrow, it won’t influence AI responses until the next model training cycle or knowledge base update. Conversely, outdated information on your site might continue to be cited by LLMs long after you’ve removed or updated it on your live site.
Understanding this lag means:
- Planning content publication timelines with longer lead times for GEO impact
- Recognising that immediate events and trends are better suited for traditional SEO, social media and paid media
- Prioritising evergreen content that remains valuable across update cycles
The speed difference doesn’t make GEO less important – it just requires different expectations and planning.
5. The power of brand mentions
In traditional SEO, the value of unlinked brand mentions has been extensively debated. Benefits are less direct, often in the form of increased brand awareness and branded search demand.
For GEO, brand mentions are unequivocally valuable. When an LLM has encountered your brand name repeatedly across authoritative sources – even without formal links – it learns that your brand is significant in your industry. This pattern recognition directly influences whether your brand gets recommended in AI-generated responses.
This means that getting your brand mentioned on high-authority sites, industry publications, podcasts (when transcribed), YouTube videos (when captioned), and community platforms like Reddit directly improves your chances of being cited by AI systems. In GEO that mention is actively teaching the LLM about your relevance and authority.
As a result, earned media and PR is now even more important. Active participation in industry conversations across multiple platforms, community engagement, and thought leadership that gets your brand associated with key industry concepts is key.
6. Old content is rarely cited by LLMs
While old content can continue to rank well in traditional SEO if it remains relevant and authoritative, LLMs show a strong bias toward recent content. AI systems preferentially cite information that appears current and up-to-date, meaning content published years ago – even if still accurate – is significantly less likely to be referenced than recently published or refreshed content.
Content refreshing isn’t just an SEO best practice for GEO – it’s essential. That comprehensive guide that still ranks well in Google might be invisible to LLMs until you update it with current data, fresh examples, and explicit date indicators like “As of 2025.” Regular content audits, updated statistics, prominent “last updated” dates, and refreshed screenshots all signal to AI systems that your expertise remains current. Where SEO allows evergreen content to coast on accumulated authority, GEO demands ongoing maintenance to stay visible.
7. The growing importance of long-tail keywords
Long-tail keywords are specific, often question-based search queries, and they have always been an important component of an effective SEO strategy, but they’re now even more important in the AI era.
Why? Because LLMs excel at understanding and answering conversational, specific queries. When someone asks an AI chatbot “What’s the best way to remove red wine stains from a wool carpet?” they’re using a long-tail query. The content that gets cited or referenced is the content that directly and comprehensively answers that specific question.
Among the most frequently sourced sites by LLMs are platforms like Quora and Reddit – places where real humans are providing real answers to real questions. These aren’t perfectly optimised corporate blog posts with keyword-stuffed meta descriptions. They’re authentic, conversational responses from people sharing their genuine experiences and expertise. To get sourced by AI systems, you need to write like a human, not a search engine.
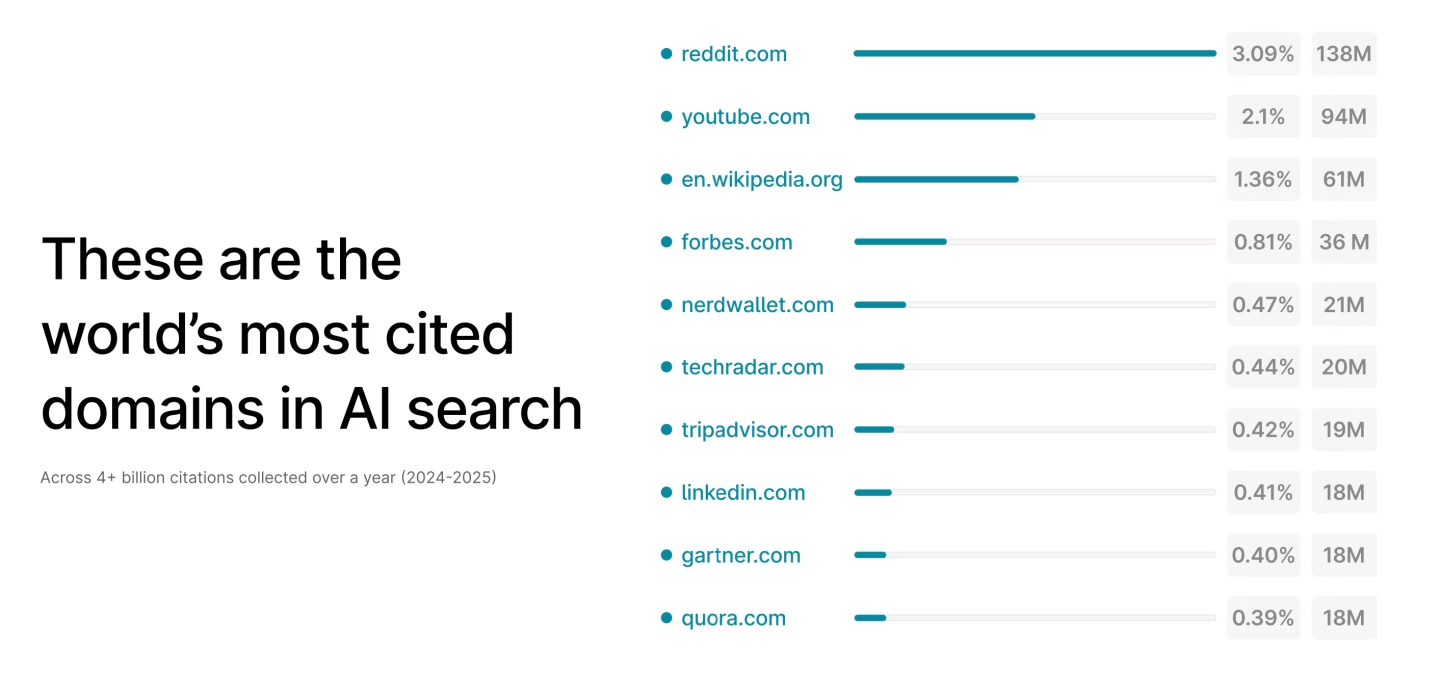
Writing for long-tail keywords means:
- Answering specific questions rather than broad topics
- Use platforms like Reddit to see what kinds of questions your audience are asking
- Using natural, conversational language that matches how people actually search
- Writing authentically as if you’re explaining something to a friend or colleague
This approach has always been good SEO because it matches user intent. Now it’s essential for GEO because it gives AI systems exactly the kind of specific, actionable information they need to help users.
How SEO, Accessibility & GEO Work Together
Here’s something that often gets overlooked in discussions about AI in SEO: accessibility and GEO are deeply interconnected. When you optimise your site for accessibility, you’re simultaneously making it easier for AI systems to understand and process your content. So when you make it easy for humans to understand your website, you’re also making it easier for the robots.
Consider these accessibility practices and their GEO benefits:
- Proper heading hierarchy (H1, H2, H3) – Helps AI understand content structure and main topics
- Descriptive alt text for images – Provides context that AI can process and reference
- Clear link text – Signals topic relevance and relationships between pages
- Semantic HTML – Communicates the purpose and type of different content elements
- Readable fonts and sufficient contrast – While primarily for humans, these practices often correlate with cleaner code
An accessible website is one that clearly communicates its content structure and meaning, exactly what AI systems need to understand and recommend your content. You don’t need special “AI optimisation” techniques; you need good web standards and accessible design.
Plus, features like transcripts for videos and audio content don’t just help users with hearing impairments, they provide AI systems with rich, indexable text that can be cited and referenced. The same applies to image descriptions, heading structures, and clear content hierarchies.
GEO Best-Practice Checklist
The core principles of good SEO remain your foundation for GEO success. However, there are additional considerations and optimisation methods specific to AI search experiences that you’ll want to layer on top of your existing strategy.
The SEO fundamentals (that also power GEO):
- Write comprehensive, answer-focused content that targets long-tail keywords
- Structure your content clearly with logical heading hierarchies
- Make your site accessible following WCAG guidelines
- Demonstrate expertise through original insights, data, and examples
- Focus on user experience across all devices
- Build topical authority by covering subjects comprehensively
- Use schema markup to help machines understand your content
- Build organic links from reputable sources
GEO-specific considerations:
- Ensure content is accessible in semantic HTML or via server-side rendering – test with JavaScript disabled to see what LLM crawlers see
- Regularly refresh content with current statistics, examples, and explicit date indicators (“As of 2025…”) to maintain visibility with LLMs
- Actively pursue brand mentions across authoritative sites, Reddit, industry publications, and community platforms – unlinked mentions teach LLMs about your relevance
- Ensure your brand appears consistently in “best of” and comparison content, both on your own site and third-party sources
- Write in natural, conversational language that mirrors how users ask questions to AI assistants
- Monitor LLM referral traffic through GA4 and track citation frequency across relevant queries
- Build a consistent brand narrative across all platforms to shape how LLMs perceive and recommend your brand
- Plan for longer lead times between content publication and GEO impact due to LLM update cycles
- Prioritise evergreen content that remains valuable across model training cycles
Measurement approach for GEO:
- Track LLM referral traffic as a distinct channel in analytics
- Monitor brand mentions and citation frequency in AI-generated responses
- Assess brand sentiment within LLM outputs
- Measure visibility against competitor mentions in relevant query spaces
Don’t fall for hype around “revolutionary” GEO tactics or expensive AI SEO tools promising overnight results. The fundamentals of creating valuable content for people remain paramount – they’ve just become more important, with some additional technical and strategic considerations for the AI era.
As Google’s Danny Sullivan noted, whether you call it SEO, GEO, AEO, or any other acronym, it’s fundamentally the same work: creating unique, valuable content for people and providing a great page experience.
Good SEO is still the foundation of good GEO – you just need to be mindful of a few additional factors along the way.
If you need some help with GEO, get in touch with the experts below 👇
Let’s discuss your project
Complete the form and we’ll be in touch the next working day.
"*" indicates required fields
FAQs
1. What is GEO in AI? What does GEO mean?
GEO stands for Generative Engine Optimisation. It focuses on shaping content so that AI-powered tools, like chatbots, AI overviews, and large language models, can easily find, understand, and reference it. Rather than targeting only traditional search rankings, GEO is about making sure your content is part of the answer when someone asks an AI a question.
2. Is GEO taking over SEO?
Not exactly. GEO is becoming more relevant as AI-led search grows, but it isn’t replacing SEO. Instead, it builds on the work that SEO already does. As more people turn to AI tools for quick, direct answers, GEO helps ensure your content still shows up in those spaces.
3. Is GEO more important than SEO?
No, GEO isn’t “more important,” but it does complement SEO. Search engines and AI models tend to favour well-structured, helpful, accessible content. So, if you’re already doing strong SEO, you’re laying the right foundations for GEO, too.
4. Is SEO dead now with AI? Will ChatGPT replace SEO?
No, SEO is not dead. AI tools can answer questions directly, sometimes without sending users to a website. That means click-through behaviour may shift, but there will always be a need for well-optimised, trustworthy content. Rather than replacing SEO, AI is pushing it to evolve, influencing how content is created, structured, and surfaced.
5. What’s the difference between SEO and GEO?
SEO = Optimising your website so it ranks on traditional search engine results pages (SERPs) like Google, Bing.
GEO = Optimising your content so it appears in or is cited by AI-driven answer engines (chatbots, AI summaries, generative models).